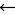Immersive technologies: the best way to deliver memorable experiences

There is an important insight for the A/V, events, entertainment and marketing industries not to be missed now that returning signs of the “normal life” are flourishing. It is that people are in need of wonderful experiences. They are in need of amazement and want to break the routine they’ve been in; whether physically or digitally. They wish to experience unique encounters and see the world in a new light. And that is what immersive technologies are all about. May it be for a special event, going shopping, or simply to the restaurant, immersive technologies transcend that need.
This blog post will try to deliver some insights and key figures regarding creating memorable experiences through immersive technologies.
What are immersive technologies?
An immersive technology is any technology that creates apparent experiences by blending the physical world with digital or simulated realities. Immersive technologies’ spectrum goes from extending reality by overlaying digital images on an environment to shutting a user out from the rest of the physical world and immersing them in a digital environment.
The two ends of the spectrum are the both famous Augmented Reality (former) and Virtual Reality (latter). Naturally, the spectrum comprises everything in between those two ends, and the different variations. Also known as Extended Reality (xR), immersive technologies refer to Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality.
Let’s go over the main immersive technologies:
Virtual Reality
Often used as an umbrella term to characterize what immersive technologies are, Virtual Reality actually has its own definition and singularity. Virtual Reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create a simulated environment. Unlike traditional user interfaces, VR places the user inside an experience. Therefore, the user no longer has the impression of interacting with the physical world but only with the created simulation.
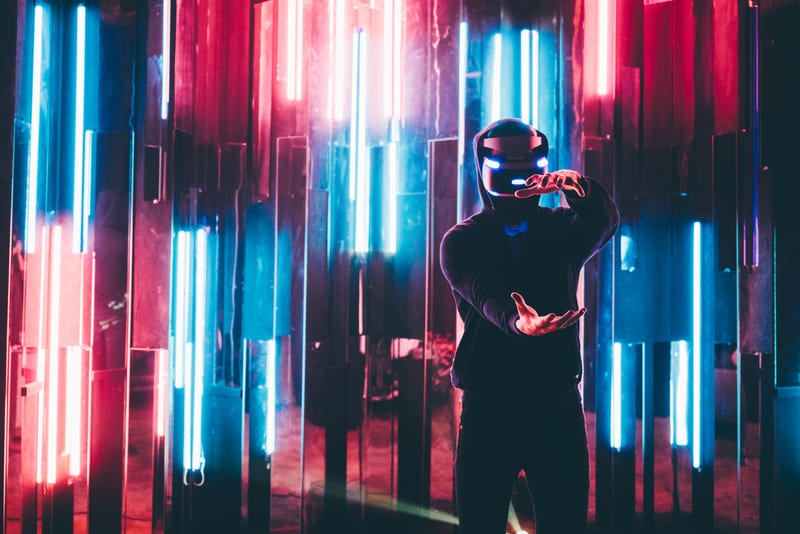
The gateway to Virtual Reality is the VR Headset. Placed directly onto the eyes, the Headset prevents the user from perceiving anything from the physical world. As a matter of fact, the immersion is absolute as the user sees only the content generated through the Headset.

The gateway to Virtual Reality is the VR Headset. Placed directly onto the eyes, the Headset prevents the user from perceiving anything from the physical world. As a matter of fact, the immersion is absolute as the user sees only the content generated through the Headset.
Many industries have understood the benefits of being immersed in environments and being able to see things at a more granular level. Thus, VR is currently used in many industries such as healthcare, automotive, education, law enforcement and, of course, gaming.
Most notable VR headsets are the Oculus Quest 2, the Valve Index, the HTC Vive or the PlayStation VR.
Augmented Reality
Let’s switch to the other end of the spectrum and onto Augmented Reality or AR. Augmented reality is characterized as a transformed version of reality in which computer-generated content is overlaid on the user’s real-world views, digital assets are therefore added to their physical environment. In that regard, AR is also defined through three essential elements: combination of physical and virtual worlds, real-time interaction and precise 3D registration of real and virtual objects.
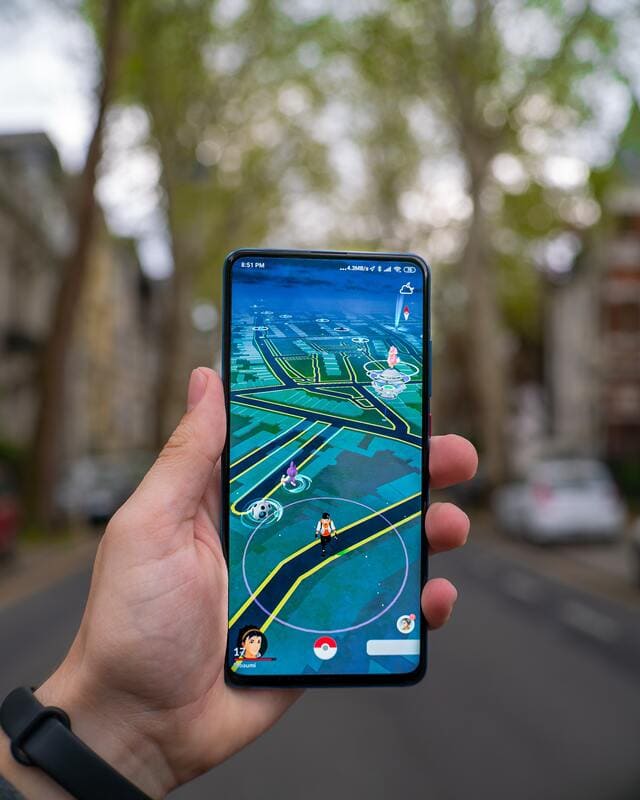

With that being said, unlike VR, augmented reality can be deployed through a myriad of different technological means; through the lens of a phone camera or with the help of a video projector for example. Most notable AR cases include the Pokemon Go App, the US Army tactical tools or Nike’s customizable sneakers. Actually, due to its technological versatility and blending with the physical world, AR is suited for countless industries.
Mixed Reality
Now that we’ve covered both ends of the spectrum, let’s dive a little deeper into the nuances of immersive technologies. Mixed reality is defined by some as the blending of both VR and AR uses. Indeed, mixed reality (MR) is the merging of real and virtual worlds to produce new environments and visualizations, where physical and digital objects co-exist and interact in real time. In other words, a headset is needed to access MR, similarly to virtual reality. However, unlike VR, MR headset doesn’t shut the user out from the physical world. On the contrary, MR headset enables the user to perceive the physical world with added layers of digital content. As familiar as that may sound compared to AR, the essential difference is the interactivity notion of MR. In fact, in mixed reality, the user is able to interact freely with its physical environment as well as controlling and interacting with superimposed digital elements. Where AR solely displays digital information, MR lets the user have complete control over the digital layers. The digital world is therefore completely mixed with the real world.
As opposed to VR and AR, mixed reality has not yet had breakthrough applications that the general public would recognize. For pop culture reference, Marvel’s Iron Man technology would be what MR resembles most in the collective consciousness.
Most notable mixed reality products include Microsoft Mesh, Microsoft Hololens and Lenovo Explorer.
As it is the most recent form of extended reality, applications for it are not numerous and still being developed.
Why immersive technologies?
Extended reality is part of the world’s most high-end and innovative technologies. And just for that, it has the potential to awe, impress, fluidify and make work almost anything. Anyone from any industry would only dream of what could be achieved should they harness its power. But anyone who’s run or even just been into a business knows that implementing new processes, let alone technology requires money, time and people. In other words, investments.
Through the following graphs and figures, we’ll try to show why immersive technologies seem to have a bright future and why industries should consider investing in them.
In fact, increased efficiency, productivity, and safety are all operational benefits of AR and VR. VR studies suggest that organizations who deploy these technologies on a broad scale are more likely to see significant operational improvements.
Which xR technology should you invest in?
It is now clear as to what immersive technologies are, as well as to why you should invest in them. But, as you know, xR comprises Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality. Realistically, chances are you won’t be able to invest in all three of them. In fact, considering resources and industry needs, very few are the companies that have developed processes enabling the implementation of xR in general. So the question now is: which immersive technology should you invest in?
We’ll try to answer this question in the following lines.
But, first of all, let’s state that we are dealing here with some of the most advanced technologies ever created. Therefore, our attempt here is never to denigrate those technologies but simply to highlight some of their specificities. Evidently, they each resolve problems that couldn’t be resolved otherwise and create experiences singular to each of them. For example, there are universities that would need MR for students to have a better understanding of the human body. But the answer given will be for a general one for most industries, businesses and creators that don’t have ultra-specific needs.
Mixed Reality: too high the cost, too few the applications (for now)
Being the most recent xR technology has a cost, in every sense of the word. As stated at the beginning of the article, MR is too recent to have had a somewhat mainstream application yet. Therefore, its use is still widely unknown by the majority of industries and the general public.
Nonetheless, MR hardware does exist, and companies can turn to manufacturers and developers to create tailored experiences (such as Microsoft or Facebook). However, as it is a brand new technology not yet democratized, the cost of developing such projects surely is high.
Virtual Reality: Perfectly shut out
VR’s biggest advantage is also one of its flaws in terms of versatility for its applications in the different industries. In fact, the gateway to VR is the headset. Which, on the one hand, provides for absolute immersion. That implies the user is completely plunged into the brand, event or show’s universe. Thus, there is maximum engagement and lasting remembrance from the user at that moment.
However, on the other hand, the headset being the only gateway to VR changes the paradigm of creating experiences. That is to say that, the means take the upper hand over the end goal. Let us explain. In the creation process for any project, you generally have an end goal or objective. “Creating a retail experience for a product launch” or “Designing a scenography for the Theatre’s 20th Anniversary” are some examples. Technology represents the means to achieve those objectives. In other words, technology should only represent a way of getting where you want to go. Whereas, in the case vR, the use of a headset is mandatory. Therefore, chances are you’re more likely to focus on how your objective can be achieved through vR more than how vR can help achieve your objectives.
And for practical and resources reasons, that realistically cannot be a fit for every kind of industry, shows or events. Let’s reuse the product launch example. A classic scenario would be an event at a flagship store or mall. The brief is to engage a maximum number of people. But if vR is deployed, then questions such as “How many headsets?”, “All at the same time?”, “How long?”, “..while people are buying?”.. These are as many questions that influence producers to adapt their objective to VR more so than the other way around.

Augmented Reality: A myriad of variations to fit any scenario
The definition of Augmented Reality was given a few lines above. However, there are several variations of ARs, and it is important to understand their differences since each is better suited to a certain application, despite the fact that they all share similar features.
The main distinction can be made between AR based on markers and AR without markers. The latter version can be divided into 4 variations: location-based AR, overlay AR, contour-based AR and projection-based AR. In total, that is two main segments adding to four variations. Out of all those options, there’s surely one form of this technology that will answer your needs.
Let’s quickly review the two main categories:
AR based on markers
Marker-based AR applications employ target pictures (markers) to place items in a specific area. The application uses these markers to decide where the 3D digital material will appear in the user’s field of vision. Instagram and Snapchat, for example, use augmented reality in the form of filters and games. As a result, this form of AR has already been integrated into human daily life as normal social activities.
AR without markers
In contrast, markerless AR allows virtual 3D objects to be positioned in the real image environment by examining the features present in the data in real time. This type of guidance relies on the hardware of any smartphone, be it the camera, GPS or accelerometer, among others, while the augmented reality software completes the job. A notable example is the Pokemon Go App.
Projection Mapping : an Augmented Reality for all
A variation stands out as particularly interesting from this markerless AR category: projection mapping. Projection mapping, also known as video mapping and spatial augmented reality, is a projection technology used to turn objects, often irregularly shaped, into a display surface for video projection. As one of the fundamental approaches to realize AR systems, projection mapping can provide xR experiences without restricting users by head-mounted/use-worn/hand-held devices. What’s more, as the digital content is projected directly onto the physical world users can see the augmentations with natural field-of-view. Moreover, with video projectors being of the essence, intuitive and reliable softwares are easily available.

A few response elements were given regarding the question of which immersive technology would be suited for most industries, should you invest in one. So, it’s been stated that mR doesn’t have enough applications and VR can not be adapted to every situation. On the other hand, augmented reality through its 5 different ‘families’ seems like the ideal candidate for anyone wanting to turn to immersive technologies. You can be sure that your project can be achieved through AR, and particularly with projection mapping, which presents all characteristics necessary for immersive experiences.

Why choose Projection Mapping?
Projection mapping is soaring and gradually making a name for itself. It is a niche process yet adaptable to any kind of event, shows or experience. While the average projection mapping service costs about US $ 10,000 per minute of 3D video content for large venues, there are perfect solutions that fit any scenario.
The following figures and numbers will try to show how projection mapping is set to become a major player of xR in the following years.
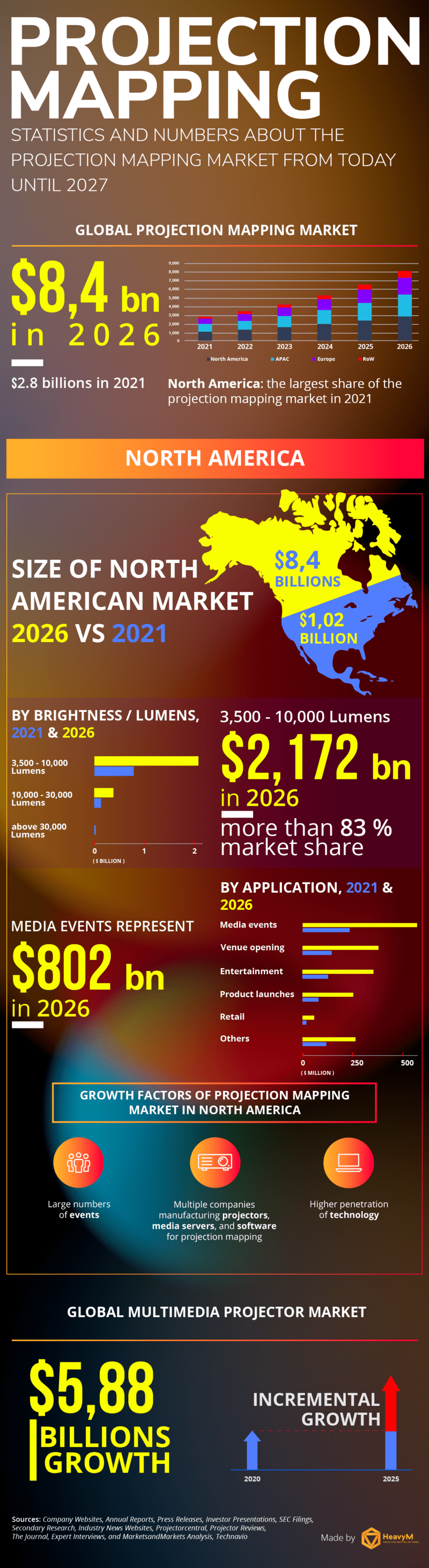
In fact, the rapid growth of the global projection mapping market is attributed to driving factors such as an increase in the use of projection mapping for media events, rising advertising spending, adoption of video mapping for product launch applications, and expanding demand for high-brightness projectors.
On the other hand, the global projector market is driven by factors such as product launches, growing demand for projectors in the education and corporate sectors, and government initiatives to support digital transformation.
Conclusion
Through the different statistics and numbers shown, the xR market is meant to explode in the following years. In fact, immersive technologies will revolutionize nearly every facet of society. They will transform business processes and the way people interact with each other. Most importantly, xR will change the way people experience life in general. Whether it is going to the restaurant, events, shopping or for a walk, xR will be implemented to better their adventure.
However, not all immersive technologies are yet suitable for every kind of project, industry or event. In fact, virtual reality and mixed reality have no equal in terms of pure immersion, but shut out the user too much to be applied to any situation.
Augmented reality, through all its different categories and mediums, seems to be a safe bet in the balance of delivering an immersive experience versus incorporating it organically in regards to an original objective. Moreover, projection mapping goes even further, as it can be applied to any kind of project. Easy-to-use and reliable solutions exist to create immersive experiences in seconds. In fact, projection mapping software HeavyM is a plug & play solution that works with any kind of projector. Users can design their vision in the software and project their reality thanks to a wide range of tools: Integrated visual library, multiple inputs, multi-projection, edge-blending, music reactivity, MIDI, NDI.. It is the way to immerse a crowd and make them live an unforgettable experience!
To be continued
Learn more about projectors
We have created a detailed guide to choosing the right projector for your needs. Discover our tips and mistakes to avoid in this guide that explains the different features step by step.
Explore the HeavyM software
HeavyM is a video mapping software that is capable of generating visual effects and projecting them on volumes, decorations or architectural elements. HeavyM is Mac and Windows compatible.