Revolutionizing Our World with 3D Mapping Technology
Brace yourself for a mind-blowing revelation: 3D mapping is here, and it’s not just some gimmicky tech trend. It’s a game-changer that’s quietly revolutionizing our world, one industry at a time. From the way we plan our cities to how we respond to disasters, 3D mapping is the unsung hero working behind the scenes to make our lives better.
But what exactly is 3D mapping, and why should you care? It boils down to making an online copy of our environment that you can almost reach out and touch. And trust me, it’s a lot cooler than it sounds.

What Is 3D Mapping?
It feels like magic—suddenly, with 3D mapping tech, understanding and moving through spaces around us has transformed dramatically. It’s the process of creating detailed, three-dimensional representations of objects, structures, and environments. Have you noticed? That breakthrough technology is reshaping industries across the board – think designing spaces in architecture or dreaming up new adventures in entertainment. 3D mapping software gives professionals the tools they need to bring their projects to life with stunning detail and accuracy.
Types of 3D Mapping Techniques
Think of creating a top-notch-3D map as choosing from a menu – lots of options, each perfect for different occasions. Some common techniques include:
- LiDAR scanning: Using laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed point clouds
- Photogrammetry: Stitching together overlapping photos to create 3D models
- Stereo vision: Using two cameras to capture depth information, similar to how our eyes work
The choice of technique depends on factors like the size of the area being mapped, the level of detail required, and the available budget.
Benefits and Applications of 3D Mapping
The benefits of 3D mapping are vast and varied. In the world of building and construction, clear chats and smart planning slash those expensive mistakes big time. For urban planners, 3D city models enable better decision-making and public engagement. Other applications include:
- Virtual tourism and heritage preservation
- Disaster response and management
- Autonomous vehicle navigation
- Gaming and entertainment
The possibilities are endless, and new uses for 3D mapping are emerging all the time.
How 3D Mapping Works
At its core, 3D mapping involves capturing spatial data from the real world and using specialized software to process it into a digital 3D model. This process typically involves several steps:
- Data acquisition: Capturing raw data using techniques like LiDAR or photogrammetry
- Data processing: Cleaning up the raw data and aligning it into a cohesive model
- Texturing and visualization: Adding realistic textures and colors to the model for better visualization
- Analysis and application: Using the 3D model for various purposes, such as measurements, simulations, or visualizations
The specific workflow can vary depending on the project requirements and the software being used. But the end result is a detailed, interactive 3D model that can be explored and analyzed in ways that were previously impossible.
3D Projection Mapping
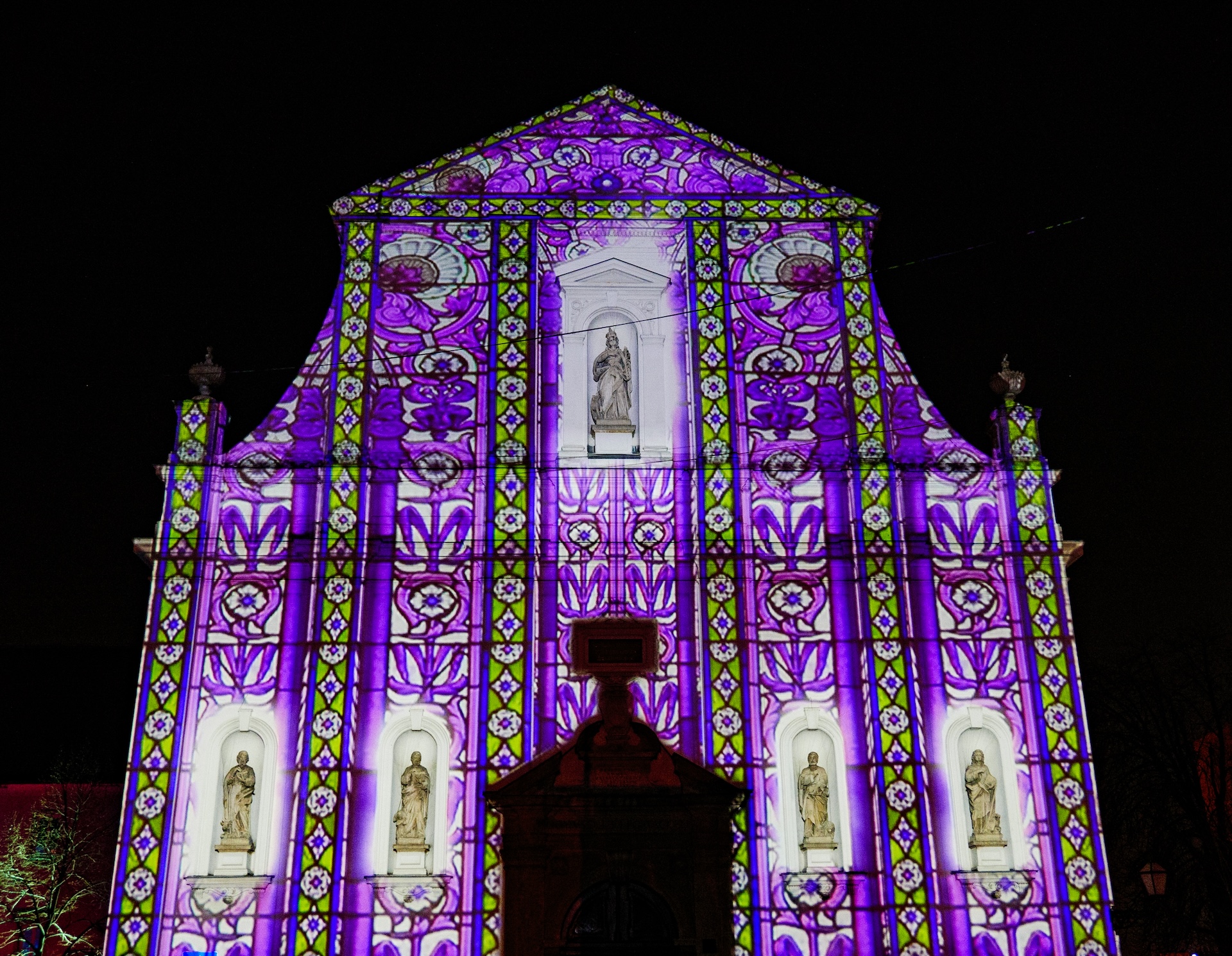

3D projection mapping, also known as video mapping or spatial augmented reality, is a special kind of 3D mapping that involves projecting video or images onto real-world objects or surfaces. It’s a stunning visual technique that can transform any surface into an interactive display. The process of 3D projection mapping starts with creating a detailed 3D model of the object or surface that will be projected onto. This model is then used to create a virtual “mask” that tells the projector where to display each pixel of the image. Next, a high-powered projector is set up in a location that gives it a clear view of the target surface. The projector is then connected to a computer running specialized software that blends the virtual mask with the desired video content. When the projector is turned on, it maps the video content onto the real-world object, creating the illusion that the object itself is moving or changing. This can be used to create stunning visual displays on buildings, cars, stage sets, and more.
Advantages of 3D Projection Mapping
One of the biggest advantages of 3D projection mapping is its flexibility. It can be used on almost any surface, from small objects to massive buildings. This makes it a popular choice for advertising, entertainment, and public art installations. Another advantage is its ability to create immersive, interactive experiences. By using motion sensors or other input devices, 3D projection mapping can respond to the movements or actions of viewers in real-time.
Cost Considerations for 3D Projection Mapping
Remember that while the magic of 3D projection mapping is undeniable, your wallet might feel a pinch from its expenses. The main expenses include:
- Projectors: High-end projectors capable of large-scale mapping can be expensive
- Software: Specialized software is required to create and control the mapping content
- Content creation: Creating custom video content for mapping can be time-consuming and costly
- Setup and operation: Setting up and running a large-scale mapping installation requires specialized skills and equipment
Despite these costs, the unique impact and engagement offered by 3D projection mapping often make it a worthwhile investment for businesses and organizations looking to create memorable experiences.
Drone 3D Mapping
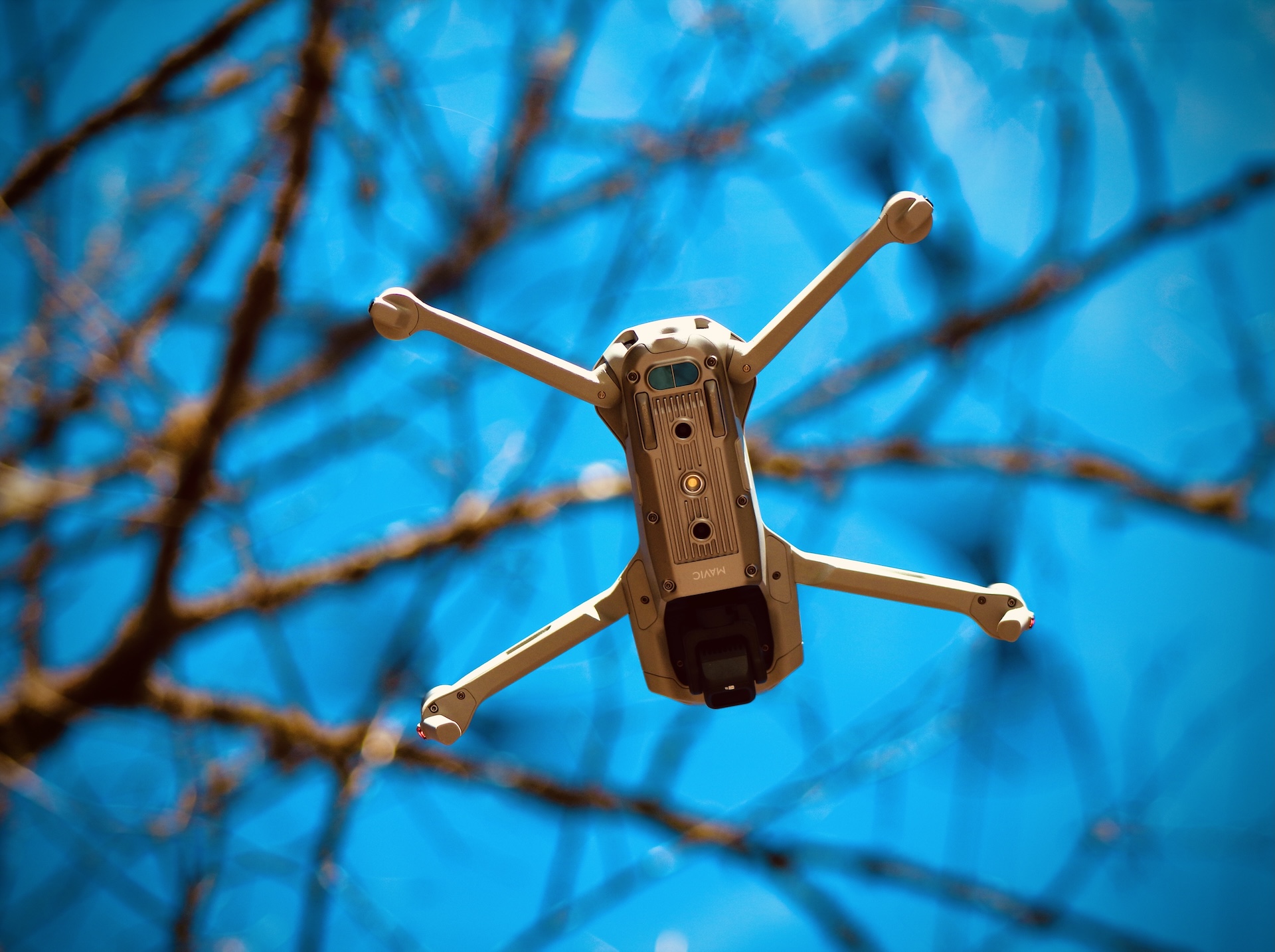

Benefits of Drone 3D Mapping
Drone mapping offers several key benefits over traditional ground-based mapping methods:
- Speed: Drones can cover large areas much faster than ground-based methods
- Accessibility: Drones can reach areas that are difficult or dangerous for humans to access
- Cost-effectiveness: Drones are often cheaper to operate than manned aircraft or ground-based surveys
- Flexibility: Drones can be equipped with a variety of sensors for different mapping needs
These benefits make drone mapping an attractive option for industries like agriculture, construction, mining, and environmental monitoring.
Drone Mapping Workflow
The typical workflow for a drone mapping project involves several steps:
- Planning: Determining the area to be mapped, the required resolution, and the appropriate drone and sensor payload
- Flight: Flying the drone over the target area in a predetermined pattern to capture overlapping images
- Data processing: Using specialized software to stitch the aerial images together into a cohesive 3D model or map
- Analysis and delivery: Analyzing the resulting data and delivering it to the client in the desired format
Many drone mapping software platforms now offer automated flight planning and data processing, making it easier than ever to get started with drone-based 3D mapping.
Applications of Drone 3D Mapping
Diving into several professions, drone technology with its knack for detailed spatial analysis has changed how we see things – quite literally. Some common use cases include:
- Surveying and land management
- Construction site monitoring and as-built documentation
- Mining and quarry management
- Precision agriculture and crop health monitoring
- Environmental monitoring and conservation
Just think – as drones evolve, so will their ability to map out our world in stunning detail from above.
3D Mapping in Urban Planning and Real Estate

Benefits of 3D Mapping in Urban Planning
3D city models offer a range of benefits for urban planners:
- Visualization: 3D models provide a realistic, immersive view of proposed developments and their impact on the surrounding area
- Analysis: 3D data can be used to analyze factors like shadow casting, wind flow, and pedestrian movement
- Collaboration: 3D models provide a common language for planners, architects, developers, and the public to communicate and collaborate
- Engagement: Interactive 3D visualizations can help engage the public in the planning process and build support for projects
By leveraging 3D mapping technology, urban planners can create more livable, sustainable, and resilient cities.
3D Mapping for Real Estate Visualization
In the real estate industry, 3D mapping is revolutionizing the way properties are marketed and sold. Some key applications include:
- Virtual tours: Interactive 3D models allow potential buyers to explore properties remotely
- Architectural visualization: 3D renderings help developers and architects communicate their vision to clients and investors
- Property analysis: 3D data can be used to analyze factors like sun exposure, views, and noise levels
- Urban context: 3D city models help buyers understand how a property fits into the surrounding neighborhood
By providing more immersive and informative experiences, 3D mapping is helping to streamline the real estate process and drive more informed decision-making.
3D Mapping in Construction and Land Surveying
Imagine how construction projects and land surveys are getting an upgrade thanks to the magic of 3D mapping technology. Some key applications include:
- Site planning: 3D terrain models help engineers optimize site layouts and grading plans
- Progress monitoring: Regular 3D scans can be used to track construction progress and identify potential issues
- As-built documentation: 3D models provide a detailed record of the completed project for maintenance and future reference
- Quantity takeoffs: 3D data can be used to quickly and accurately calculate material quantities and costs
By providing more accurate and efficient ways to plan, execute, and document projects, 3D mapping is helping to reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance safety in the construction industry.
Future Trends in 3D Mapping

Advancements in 3D Mapping Technology
One of the biggest drivers of innovation in 3D mapping is the rapid advancement of the underlying technologies. Some key areas to watch include:
- Sensors: New sensors like solid-state LiDAR and hyperspectral cameras are enabling faster, more detailed, and more affordable data capture
- Platforms: Advances in drone, satellite, and autonomous vehicle technology are expanding the reach and flexibility of mapping platforms
- Processing: Cloud computing and GPU acceleration are enabling faster, more automated data processing and analysis
- Visualization: Virtual and augmented reality technologies are creating new possibilities for immersive, interactive 3D experiences
As these technologies continue to mature, they’re opening up new applications and use cases for 3D mapping across a wide range of industries.